Toxicity: Fishing for protective compounds
Cancer treatments have become increasingly effective over the past few decades, but the chemotherapy drugs that kill tumour cells also damage healthy tissues. This can lead to serious side effects that go on to impair the quality of life of patients after recovery. For instance, cisplatin, a drug used to treat testicular cancer, is toxic to kidneys and hair cells in the ear that are necessary for hearing processes (Daugaard, 1990; Einhorn, 2002; Rybak and Ramkumar, 2007; Pabla and Dong, 2008; Lanvers-Kaminsky et al., 2017). Now, in eLife, Jason Berman and colleagues in institutions across Canada – including Jamie Wertman as first author – report the results of a study screening for compounds that reduce the toxicity of cisplatin (Wertman et al., 2020).
To do so, the team enlisted the zebrafish Danio rerio, a tiny freshwater tropical fish similar to humans at the molecular level, but can be bred cheaply and quickly (Schartl, 2014). It has become an exceptionally important in vivo model for biomedical research, especially to test the toxicity of drugs such as cisplatin or the antibiotics gentamicin (Rocha-Sanchez et al., 2018; Swanhart et al., 2011). Indeed, even at the larval stage, the fish has easily accessible hair cells in its lateral line (a sensory organ under the skin), and a primitive, anatomically simple kidney (Swanhart et al., 2011).
Wertman et al. examined whether 1200 compounds could protect the kidneys and lateral line hair cells of zebrafish larvae against the toxic effects of cisplatin. The screening highlighted 22 molecules, including two that offered the highest levels of protection: dopamine, a compound that nerve cells use to communicate, and L-mimosine, a rare plant non-protein amino acid similar to the amino acid tyrosine (Figure 1). Their protective potential was confirmed in vivo in the primitive kidney and another population of hair cells in zebrafish larvae. In addition, dopamine and L-mimosine did not keep cisplatin from killing cancer cells grown in the laboratory.
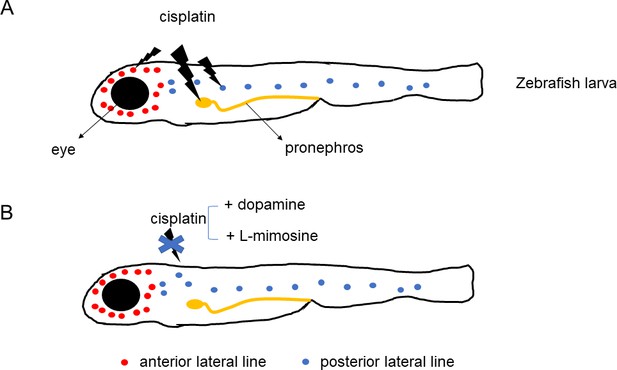
Protective effects of dopamine and L-mimosine against the cancer drug cisplatin.
Treatment of zebrafish larvae with cisplatin (panel A) impairs the function (lightning bolt icon) of the fish's primitive kidney (pronephros), and of its anterior and posterior lateral line – the organs that display hair cells similar to the ones found in ears. Application of dopamine or L-mimosine (panel B) suppresses the toxic effects of cisplatin.
The next step would be to investigate how dopamine and L-mimosine perform this protective role. Organic cation transporters are a family of proteins that help to carry molecules – including dopamine – into cells. In their absence, cisplatin is less toxic for ears and kidneys (Hucke et al., 2019). It is therefore possible that dopamine and L-mimosine compete with cisplatin for access to the transporters: this would result in fewer cisplatin molecules accessing kidney and ear hair cells, ultimately protecting the organs against the cancer drug.
Finally, it is essential to demonstrate that dopamine and L-mimosine do not impair the anticancer activity of cisplatin in vivo, which could also be done in zebrafish larvae. In addition, this animal model could be useful to study neurotoxicity, another potential side effect of the drug. This would allow scientists to investigate whether the two compounds only protect specific organs, or globally interfere with cisplatin activity.
Confirming that dopamine and L-mimosine preserve the anticancer properties of cisplatin in vivo, together with fully understanding how they shield ears and kidneys from the drug’s toxicity should help to develop protective therapies. Ultimately, this would allow more aggressive cancer chemotherapy to be performed, and improve the quality of life of cancer survivors.
References
-
Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: experimental and clinical studiesDanish Medical Bulletin 37:1–12.
-
Drug-induced ototoxicity: mechanisms, pharmacogenetics, and protective strategiesClinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 101:491–500.https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.603
-
Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategiesKidney International 73:994–1007.https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002786
-
Beyond the zebrafish: diverse fish species for modeling human diseaseDisease Models & Mechanisms 7:181–192.https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.012245
-
Zebrafish kidney development: basic science to translational researchBirth Defects Research Part C: Embryo Today: Reviews 93:141–156.https://doi.org/10.1002/bdrc.20209
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: September 3, 2020 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2020, Ciarimboli
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 581
- views
-
- 32
- downloads
-
- 0
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Cancer Biology
- Cell Biology
Internalization from the cell membrane and endosomal trafficking of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are important regulators of signaling in normal cells that can frequently be disrupted in cancer. The adrenal tumor pheochromocytoma (PCC) can be caused by activating mutations of the rearranged during transfection (RET) receptor tyrosine kinase, or inactivation of TMEM127, a transmembrane tumor suppressor implicated in trafficking of endosomal cargos. However, the role of aberrant receptor trafficking in PCC is not well understood. Here, we show that loss of TMEM127 causes wildtype RET protein accumulation on the cell surface, where increased receptor density facilitates constitutive ligand-independent activity and downstream signaling, driving cell proliferation. Loss of TMEM127 altered normal cell membrane organization and recruitment and stabilization of membrane protein complexes, impaired assembly, and maturation of clathrin-coated pits, and reduced internalization and degradation of cell surface RET. In addition to RTKs, TMEM127 depletion also promoted surface accumulation of several other transmembrane proteins, suggesting it may cause global defects in surface protein activity and function. Together, our data identify TMEM127 as an important determinant of membrane organization including membrane protein diffusability and protein complex assembly and provide a novel paradigm for oncogenesis in PCC where altered membrane dynamics promotes cell surface accumulation and constitutive activity of growth factor receptors to drive aberrant signaling and promote transformation.
-
- Cancer Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
Enhancers are critical for regulating tissue-specific gene expression, and genetic variants within enhancer regions have been suggested to contribute to various cancer-related processes, including therapeutic resistance. However, the precise mechanisms remain elusive. Using a well-defined drug-gene pair, we identified an enhancer region for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD, DPYD gene) expression that is relevant to the metabolism of the anti-cancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). Using reporter systems, CRISPR genome-edited cell models, and human liver specimens, we demonstrated in vitro and vivo that genotype status for the common germline variant (rs4294451; 27% global minor allele frequency) located within this novel enhancer controls DPYD transcription and alters resistance to 5-FU. The variant genotype increases recruitment of the transcription factor CEBPB to the enhancer and alters the level of direct interactions between the enhancer and DPYD promoter. Our data provide insight into the regulatory mechanisms controlling sensitivity and resistance to 5-FU.






